Get started with the Canonical Identity Platform
Whatever your deployment – whether it’s on Kubernetes, VMs, or across clouds – you likely need a reliable way to manage authentication, authorization, and often single sign-on (SSO).
Traditionally, setting this up involves assembling and configuring multiple components, securing and scaling them, and ensuring seamless integration – a process that demands deep, domain-specific expertise. And if it’s not done right, the consequences can be serious: from misconfigurations that break user access to security vulnerabilities that put your entire system at risk.
Enter the Canonical Identity Platform: a composable identity broker and identity provider built on trusted open source projects from Ory, PostgreSQL, and Traefik Labs. With expert operations and configurations encoded in reusable operators called ‘charms’, and a powerful model-driven deployment engine in Juju, the Identity Platform eliminates complexity and lets you focus on your users, not your infrastructure.
What you’ll need
This tutorial assumes you have
- A Juju controller (v3.1+) bootstrapped on a MicroK8s cluster with
metallbaddon or Canonical Kubernetes (v1.25.0+) that is ready to use. See, e.g., Juju | Set up your deployment - local testing and development. - The Terraform CLI. See Hashicorp | Install Terraform (v1.5.0+).
What you’ll do
In this tutorial you will deploy the Identity Platform and use it to provide SSO to an OIDC compatible charm.
Deploy the Identity Platform
To set up the Canonical Identity Platform, you’ll need to deploy, configure, and integrate its component charms. We’ve taken advantage of the Terraform Provider for Juju to create a Terraform plan that automates this process for you.
Start by cloning the GitHub repository that hosts these Terraform modules:
git clone https://github.com/canonical/iam-bundle-integration.git && cd iam-bundle-integration
git checkout v1.0.2
Then navigate to the tutorial example and deploy the stack:
terraform -chdir=examples/tutorial init
terraform -chdir=examples/tutorial apply -auto-approve
Expand to view the Terraform plan
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
<= read (data resources)
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# juju_integration.traefik_certs will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "traefik_certs" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "certificates"
+ name = "self-signed-certificates"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "certificates"
+ name = "traefik-public"
}
}
# juju_model.core will be created
+ resource "juju_model" "core" {
+ credential = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "core"
+ type = (known after apply)
+ uuid = (known after apply)
}
# juju_model.iam will be created
+ resource "juju_model" "iam" {
+ credential = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "iam"
+ type = (known after apply)
+ uuid = (known after apply)
}
# juju_offer.postgresql will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "postgresql" {
+ application_name = "postgresql-k8s"
+ endpoints = [
+ "database",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "postgresql"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# juju_offer.send_ca_certificate will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "send_ca_certificate" {
+ application_name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ endpoints = [
+ "send-ca-cert",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "send-ca-cert"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# juju_offer.traefik_route will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "traefik_route" {
+ application_name = "traefik-public"
+ endpoints = [
+ "traefik-route",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "traefik-route"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.certificates.juju_application.self-signed-certificates will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "self-signed-certificates" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = false
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@24.04"
+ channel = "1/stable"
+ name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.certificates.juju_offer.certificates will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "certificates" {
+ application_name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ endpoints = [
+ "certificates",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "certificates"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.certificates.juju_offer.send_ca_cert will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "send_ca_cert" {
+ application_name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ endpoints = [
+ "send-ca-cert",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "send-ca-cert"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.data.juju_model.this will be read during apply
# (config refers to values not yet known)
<= data "juju_model" "this" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ uuid = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.data.juju_offer.ca_certificate will be read during apply
# (config refers to values not yet known)
<= data "juju_offer" "ca_certificate" {
+ application_name = (known after apply)
+ endpoints = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.data.juju_offer.database will be read during apply
# (config refers to values not yet known)
<= data "juju_offer" "database" {
+ application_name = (known after apply)
+ endpoints = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.data.juju_offer.traefik_route will be read during apply
# (config refers to values not yet known)
<= data "juju_offer" "traefik_route" {
+ application_name = (known after apply)
+ endpoints = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.hydra_database will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "hydra_database" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "pg-database"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.hydra_login_ui_ui_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "hydra_login_ui_ui_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ui-endpoint-info"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ui-endpoint-info"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.hydra_public_route will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "hydra_public_route" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "public-route"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_database will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_database" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "pg-database"
+ name = "kratos"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_hydra_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_hydra_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "hydra-endpoint-info"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "hydra-endpoint-info"
+ name = "kratos"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_login_ui_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_login_ui_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "kratos-info"
+ name = "kratos"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "kratos-info"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_login_ui_ui_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_login_ui_ui_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ui-endpoint-info"
+ name = "kratos"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ui-endpoint-info"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_public_route will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_public_route" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "public-route"
+ name = "kratos"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.login_ui_hydra_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "login_ui_hydra_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "hydra-endpoint-info"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "hydra-endpoint-info"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.login_ui_public_route will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "login_ui_public_route" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "public-route"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_offer.kratos_info_offer will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "kratos_info_offer" {
+ application_name = "kratos"
+ endpoints = [
+ "kratos-info",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "kratos-info-offer"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.postgresql.juju_application.k8s_postgresql will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "k8s_postgresql" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "postgresql-k8s"
+ resources = {}
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ storage_directives = {
+ "pgdata" = "10G"
}
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "14/edge"
+ name = "postgresql-k8s"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.traefik.juju_application.traefik will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "traefik" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "traefik-public"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ storage_directives = {}
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = (known after apply)
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "traefik-k8s"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.module.hydra.juju_application.application will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "application" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "hydra"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "hydra"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.module.hydra.juju_offer.oauth_offer will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "oauth_offer" {
+ application_name = "hydra"
+ endpoints = [
+ "oauth",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "oauth-offer"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.module.kratos.juju_application.application will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "application" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "kratos"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "kratos"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.module.login_ui.juju_application.application will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "application" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "login-ui"
+ resources = {
+ "oci-image" = "ghcr.io/canonical/identity-platform-login-ui:v0.24.2"
}
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "identity-platform-login-ui-operator"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
Plan: 26 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Terraform will create two Juju models (workspaces). These models are implicitly associated with your existing controller and MicroK8s cloud and hold your deployed, configured, and integrated Identify Platform charmed applications and their charmed dependencies.
This process will take several minutes, depending on your hardware and network speed.
The iam model contains all the crucial identity applications:
- Charmed Ory Hydra: the OAuth/OIDC server
- Charmed Ory Kratos: the user management and authentication component
- Login UI operator: a middleware which routes calls between the different services and serves the login/error pages
And the core model contains all of their shared dependencies:
- Charmed Postgresql: the SQL database of choice
- Charmed Traefik: which will be used for ingress
- Self Signed Certificates: for managing the TLS certificates that our ingress will use.
You can switch between those models using juju switch <iam|core> and track the progress of your deployment by running:
juju status --watch 1s
This command displays the status of the installation and information about the model, like IP addresses, ports, versions etc.
Your deployment is ready when juju status displays the following output:
Model Controller Cloud/Region Version SLA Timestamp
iam my-controller microk8s/localhost 3.6.13 unsupported 16:37:26+01:00
SAAS Status Store URL
postgresql active local admin/core.postgresql
traefik-route active local admin/core.traefik-route
App Version Status Scale Charm Channel Rev Address Exposed Message
hydra v2.3.0 active 1 hydra latest/stable 395 10.152.183.127 no
kratos v1.3.1 active 1 kratos latest/stable 565 10.152.183.75 no
login-ui 0.24.2 active 1 identity-platform-login-ui-operator latest/stable 197 10.152.183.135 no
Unit Workload Agent Address Ports Message
hydra/0* active idle 10.1.57.184
kratos/0* active idle 10.1.57.183
login-ui/0* active idle 10.1.57.185
Offer Application Charm Rev Connected Endpoint Interface Role
kratos-info-offer kratos kratos 565 0/0 kratos-info kratos_info provider
oauth-offer hydra hydra 395 0/0 oauth oauth provider
Set up the identity provider
So far, you’ve deployed the Canonical Identity Platform core components, but you still need a way to log in.
You have two choices: create accounts right away using the built-in identity provider, or connect an external provider (e.g. Google, Entra ID, GitHub…). You can choose to use just one of these options – either local or external – or combine them to let users sign in through both.
Use the built-in identity provider
The Identity Platform comes with a built-in identity provider, allowing you to manage user accounts internally without relying on a third-party service. You can also let your users authenticate both with external providers and the local one.
The local identity provider feature is enabled by default in Charmed Kratos.
At this stage, you can create your personal admin account:
juju run kratos/0 create-admin-account email=<your-email> username=<username>
After the account is created, use the provided password reset link to set your password and complete the setup.
Congratulations, you’re all set to use the built-in identity provider to sign in.
Connect the Canonical Identity Platform to an external identity provider
This option assumes that you have a GitHub account.
To use an external identity provider alongside the local one, you can leverage Kratos External IdP Integrator.
In this step we are going to:
- create a GitHub confidential client and configure it with Kratos redirect URL
- extend our Identity Platform deployment by adding the integrator charm
- connect the Identity Platform with GitHub.
First, we need to know our deployment’s redirect_uri. Get the Kratos base URL provided by the ingress integration:
juju show-unit kratos/0 --endpoint public-route
It will look similar to https://10.64.140.43.
The redirect_uri should be: <kratos-base-url>/self-service/methods/oidc/callback/github.
We will use this callback URL to configure your client in GitHub.
Next, go to GitHub developer settings and register a new OAuth application. Provide the Kratos redirect URL as the authorization callback URL. Take note of your newly generated client ID and secret.
See more: GitHub | Create an OAuth App
We can now configure the Identity Platform with the GitHub client credentials.
Start by creating a vars.tfvars file in the examples/tutorial directory
where you specify the GitHub configuration and enable the integrator charm:
enable_kratos_external_idp_integrator = true
kratos_external_idp_integrator = {
config = {
client_id = "<client-id>"
client_secret = "<client-secret>"
provider = "github"
provider_id = "github"
scope = "user:email"
}
}
Finally, re-apply the module to deploy Kratos External IdP Integrator:
terraform -chdir=examples/tutorial apply -var-file="./vars.tfvars"
See more: Charmhub | Kratos External IdP Integrator | Integrate with external identity providers
This integrator charm enables Charmed Kratos to work with an external identity provider.
After a while, the kratos-external-idp-integrator status will change to active.
This means that GitHub has been added as a Kratos sign-in provider.
Congratulations, your deployment now uses GitHub as your external identity provider.
Use the Identity Platform to provide SSO
Now that our identity broker is ready and the Platform can also serve as an identity provider, we can provide SSO to an application. For this purpose we are going to use Grafana. To deploy Charmed Grafana, run:
juju switch iam
juju deploy grafana-k8s
This command deploys Charmed Grafana in the same model as the Identity Platform.
The newly deployed Grafana requires ingress in order to properly integrate with the Identity Platform. We can leverage the existing Traefik instance for this purpose. You can integrate Charmed Grafana with Traefik by running:
juju integrate grafana-k8s:ingress admin/core.traefik-route
Now, you can connect Grafana with the Identity Platform. To do this we need to integrate Grafana with the OIDC server, Hydra:
juju integrate grafana-k8s:oauth hydra
This command registers Grafana as an OIDC client in Hydra and configures Grafana to use the Canonical Identity Platform as an authentication provider.
Finally, integrate Grafana with the self-signed-certificates charmed application:
juju integrate grafana-k8s:receive-ca-cert admin/core.send-ca-cert
Once all applications are ready, log in to Grafana through GitHub or with your admin user created in the previous step.
Log in to Grafana through the Identity Platform
To access the Grafana dashboard:
-
Get the traefik-public IP:
juju show-unit grafana-k8s/0 | yq e '.["grafana-k8s/0"].relation-info[] | select(.endpoint=="ingress") | .application-data.external_host' - -
Use the traefik-public IP to access the Grafana dashboard at
https://<traefik_public_ip>/iam-grafana-k8s.
Upon navigating to the URL you will be presented with the following login screen:
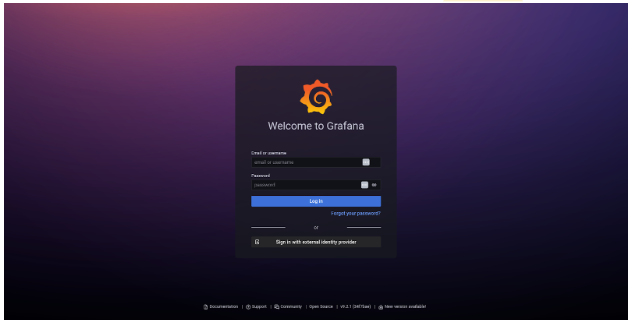
Click on Sign in with external identity provider and, after you trust the self-signed TLS cert, you will be redirected to the login page where you can select to authenticate with GitHub or your local user:
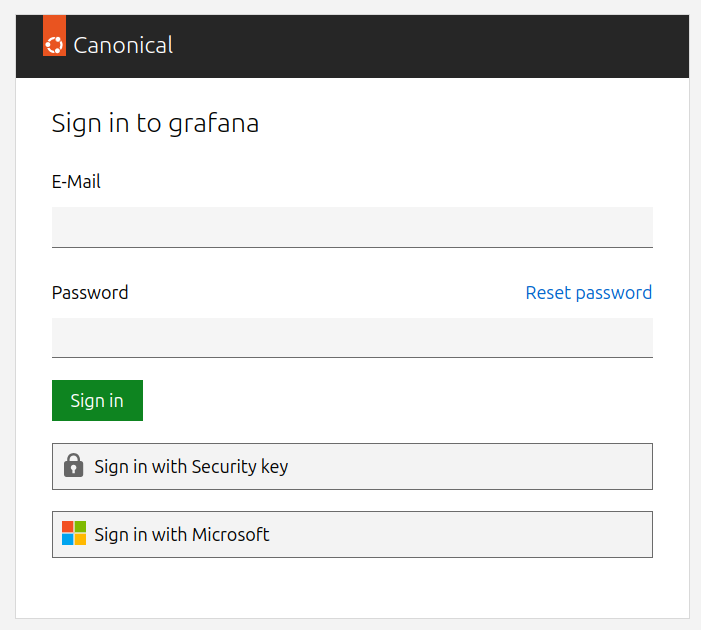
After a successful login, you will be redirected back to Grafana. Congratulations, your GitHub users and locally created accounts can now access your Grafana dashboards!
See more: Charmhub | Identity Plaform
Tear things down
To clean up the resources created during this tutorial, run:
terraform -chdir=examples/tutorial destroy
This will remove all charmed applications and destroy the Juju models that were provisioned as part of the deployment.