I couldn’t reproduce it last night. I managed to get it all going. Thanx for looking in to it though.
Update is that I have not been able to reproduce my error. Possibly something local to my client might have caused the above.
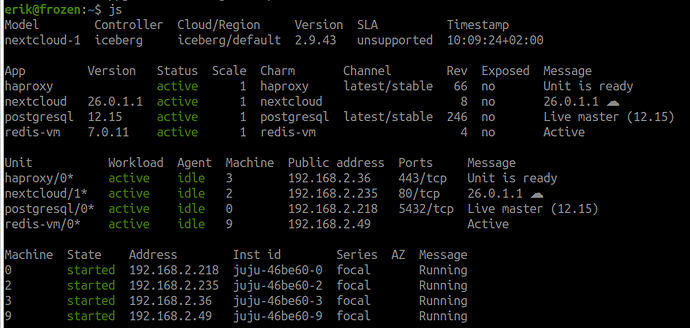
So, I’m about to figure out how to replace me old postgresql for Nextcloud.
My current deploy looks like this, with the “old” reactive postgresql charm on revision 246.
The relation/integration that is used for the old versions of the charm is: postgresql:db <-> nextcloud:db on the interface: postgresql
In Nextcloud metadata.yaml
requires:
db:
interface: pgsql
The new charm needs to move to a new relation to work with postgresql:
database:
interface: postgresql_client
limit: 1
I have a tricky situation now, since I can’t seem to re-deploy the old charm (revision 246) charm, since its no longer available in the store. Since I would like to reproduce the deployment, to test my migration process. This means I would need access to the old version of the charm postgresql.
Where can I find it?
My strategy for migrating from old to new isn’t 100% cleared out, but I guess this is what I need to find out. I have found this draft material which I will use: Charmed PostgreSQL How-to - Migrate from Legacy (overview) @tmihoc
sorry, all this discussion is out of scope of this tutorial
please ask you question on: Mattermost
For the history:
I have a tricky situation now, since I can’t seem to re-deploy the old charm (revision 246) charm, since its no longer available in the store.
It is available in the store, but you have faced a bug Bug #2020899 “cannot resolve charm or bundle “mongodb”: resolvin...” : Bugs : MongoDB Charm (the legacy charm should be installable again from latest/stable channel soon). The possible workaround there is to define “series” on deployment.
The manual How-to Migrate is on the way, the link point to the proper placeholder.
I was reading through this and noticed that the link “The location of a charm library inside a charm” is to an archived page and inaccessible on the production docs.
The link should now be pointing to a subsection inside of the general “Library” explanation, which is here: Library
Another thing I noticed was that the postgresql-k8s charm itself required --trust to be deployed. I found this out by looking at the charm documentation and saw that the machine charm can be run without --trust but the k8s charm requires some changes to service accounts (maybe? or at least something with privileges).
So the line:
juju deploy postgresql-k8s --channel=14/stable
Should become
juju deploy postgresql-k8s --channel=14/stable --trustI recently tested these instructions. From what I remember, the code as given works – so, without trust. I’ll check again though.
Fixed, thanks!
I think what I found was that it would deploy, but end up at a “blocked” state. It wasn’t until I dived into the logs that I saw it trying to do things with service accounts and then I found the postgresql-k8s charm page itself (Charmhub | Deploy Charmed PostgreSQL K8s using Charmhub - The Open Operator Collection) had a --trust in its tutorial.
Done, thanks!
key is never used in the loop of the above code. If there is no reason to evaluate the key attribute we may want to make the code easier to understand, e.g. like this:
def fetch_postgres_relation_data(self) -> dict:
relations = self.database.fetch_relation_data()
logger.debug("Got following database data: %s", relations)
for data in relations.values():
if not data:
continue
logger.info("New PSQL database endpoint is %s", data["endpoints"])
...
Done, thanks!
The method fetch_postgres_relation_data in the charms.py is broken from lection 4 on.
https://github.com/canonical/juju-sdk-tutorial-k8s/blob/04_integrate_with_psql/src/charm.py#L107C1-L131C28
def fetch_postgres_relation_data(self) -> dict:
"""Fetch postgres relation data.
This function retrieves relation data from a postgres database using
the `fetch_relation_data` method of the `database` object. The retrieved data is
then logged for debugging purposes, and any non-empty data is processed to extract
endpoint information, username, and password. This processed data is then returned as
a dictionary. If no data is retrieved, the unit is set to waiting status and
the program exits with a zero status code."""
relations = self.database.fetch_relation_data()
logger.debug("Got following database data: %s", relations)
for data in relations.values():
if not data:
continue
logger.info("New PSQL database endpoint is %s", data["endpoints"])
host, port = val["endpoints"].split(":")
db_data = {
"db_host": host,
"db_port": port,
"db_username": val["username"],
"db_password": val["password"],
}
return db_data
self.unit.status = WaitingStatus("Waiting for database relation")
raise SystemExit(0)
should be
def fetch_postgres_relation_data(self) -> dict:
"""Fetch postgres relation data.
This function retrieves relation data from a postgres database using
the `fetch_relation_data` method of the `database` object. The retrieved data is
then logged for debugging purposes, and any non-empty data is processed to extract
endpoint information, username, and password. This processed data is then returned as
a dictionary. If no data is retrieved, the unit is set to waiting status and
the program exits with a zero status code."""
relations = self.database.fetch_relation_data()
logger.debug("Got following database data: %s", relations)
for data in relations.values():
if not data:
continue
logger.info("New PSQL database endpoint is %s", data["endpoints"])
host, port = data["endpoints"].split(":")
db_data = {
"db_host": host,
"db_port": port,
"db_username": data["username"],
"db_password": data["password"],
}
return db_data
self.unit.status = WaitingStatus("Waiting for database relation")
raise SystemExit(0)
(Variable name val is not defined and should be data)
I already changed that in the doc post. Should I do a PR for the Github repo or directly pushing it to the branch?
@bschimke95 The process we’ve followed so far is direct push to the branch + updates to the subsequent branches by successive merge (switch to the next branch, merge the previous branch into it, repeat).
Done, thanks!