Get started with the Canonical Identity and Access Proxy
Applications that do not conform to OAuth 2.0 and OIDC standards or don’t offer built-in access control need to be secured in alternative ways.
The Canonical Identity and Access Proxy (IAP) fills that security gap. It intercepts incoming requests at the ingress level and delegates the authentication process to the Canonical Identity Platform before allowing traffic to reach your workload.
The solution is based on open source products from Ory, Traefik Labs, and OAuth2 Proxy - a Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) Sandbox project.
In this architecture, the enforcement point is Traefik, while the decision-making is handled by OAuth2 Proxy. As a widely adopted, community-driven tool, OAuth2 Proxy provides a robust, standard-compliant bridge between the Identity Platform’s OIDC provider (Ory Hydra) and your ingress controller, ensuring a secure and cloud-native approach to protecting your applications.
What you’ll need
This tutorial assumes you have
- A Juju controller (v3.1+) bootstrapped on a MicroK8s cluster with
metallbaddon or Canonical Kubernetes (v1.25.0+) that is ready to use. See, e.g., Juju | Set up your deployment - local testing and development. - The Terraform CLI. See Hashicorp | Install Terraform (v1.5.0+)
- MinIO Kubernetes Plugin enabled. See more: Enable MinIO plugin on Microk8s
- MinIO credentials and S3 endpoint necessary to configure Spark History Server.
What you’ll do
In this tutorial, you will use Terraform to provision the Identity Platform and OAuth2 Proxy, then deploy a sample workload with Juju to validate the access control integration.
Deploy the Identity Platform & Identity and Access Proxy
To set up the Canonical Identity Platform, you’ll need to deploy, configure, and integrate its component charms. We’ve taken advantage of the Terraform Provider for Juju to create a Terraform plan that automates this process for you.
Start by cloning the GitHub repository that hosts these Terraform modules:
git clone https://github.com/canonical/iam-bundle-integration.git && cd iam-bundle-integration
git checkout v1.1.0
Then, navigate to the auth-proxy example and deploy the stack:
terraform -chdir=examples/auth-proxy init
terraform -chdir=examples/auth-proxy apply -auto-approve
Expand to view the Terraform plan
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
<= read (data resources)
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# juju_integration.oauth2_proxy_certs will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "oauth2_proxy_certs" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "receive-ca-cert"
+ name = "oauth2-proxy"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# juju_integration.oauth2_proxy_forward_auth will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "oauth2_proxy_forward_auth" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "forward-auth"
+ name = "oauth2-proxy"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# juju_integration.oauth2_proxy_ingress will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "oauth2_proxy_ingress" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ingress"
+ name = "oauth2-proxy"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# juju_integration.oauth2_proxy_oauth will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "oauth2_proxy_oauth" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "oauth"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "oauth"
+ name = "oauth2-proxy"
}
}
# juju_integration.traefik_certs will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "traefik_certs" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "certificates"
+ name = "self-signed-certificates"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "certificates"
+ name = "traefik-public"
}
}
# juju_model.core will be created
+ resource "juju_model" "core" {
+ credential = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "core"
+ type = (known after apply)
+ uuid = (known after apply)
}
# juju_model.iam will be created
+ resource "juju_model" "iam" {
+ credential = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "iam"
+ type = (known after apply)
+ uuid = (known after apply)
}
# juju_offer.forward_auth will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "forward_auth" {
+ application_name = "traefik-public"
+ endpoints = [
+ "experimental-forward-auth",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "forward-auth"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# juju_offer.ingress will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "ingress" {
+ application_name = "traefik-public"
+ endpoints = [
+ "ingress",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "ingress"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# juju_offer.postgresql will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "postgresql" {
+ application_name = "postgresql-k8s"
+ endpoints = [
+ "database",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "postgresql"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# juju_offer.send_ca_certificate will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "send_ca_certificate" {
+ application_name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ endpoints = [
+ "send-ca-cert",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "send-ca-cert"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# juju_offer.traefik_route will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "traefik_route" {
+ application_name = "traefik-public"
+ endpoints = [
+ "traefik-route",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "traefik-route"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.certificates.juju_application.self-signed-certificates will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "self-signed-certificates" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = false
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@24.04"
+ channel = "1/stable"
+ name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.certificates.juju_offer.certificates will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "certificates" {
+ application_name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ endpoints = [
+ "certificates",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "certificates"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.certificates.juju_offer.send_ca_cert will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "send_ca_cert" {
+ application_name = "self-signed-certificates"
+ endpoints = [
+ "send-ca-cert",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "send-ca-cert"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.data.juju_model.this will be read during apply
# (config refers to values not yet known)
<= data "juju_model" "this" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ uuid = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.data.juju_offer.ca_certificate will be read during apply
# (config refers to values not yet known)
<= data "juju_offer" "ca_certificate" {
+ application_name = (known after apply)
+ endpoints = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.data.juju_offer.database will be read during apply
# (config refers to values not yet known)
<= data "juju_offer" "database" {
+ application_name = (known after apply)
+ endpoints = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.data.juju_offer.traefik_route will be read during apply
# (config refers to values not yet known)
<= data "juju_offer" "traefik_route" {
+ application_name = (known after apply)
+ endpoints = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.hydra_database will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "hydra_database" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "pg-database"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.hydra_login_ui_ui_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "hydra_login_ui_ui_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ui-endpoint-info"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ui-endpoint-info"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.hydra_public_route will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "hydra_public_route" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "public-route"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_database will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_database" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "pg-database"
+ name = "kratos"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_hydra_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_hydra_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "hydra-endpoint-info"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "hydra-endpoint-info"
+ name = "kratos"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_login_ui_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_login_ui_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "kratos-info"
+ name = "kratos"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "kratos-info"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_login_ui_ui_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_login_ui_ui_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ui-endpoint-info"
+ name = "kratos"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "ui-endpoint-info"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.kratos_public_route will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "kratos_public_route" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "public-route"
+ name = "kratos"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.login_ui_hydra_info will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "login_ui_hydra_info" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "hydra-endpoint-info"
+ name = "hydra"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = "hydra-endpoint-info"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
}
# module.iam.juju_integration.login_ui_public_route will be created
+ resource "juju_integration" "login_ui_public_route" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ application {
+ endpoint = "public-route"
+ name = "login-ui"
}
+ application {
+ endpoint = (known after apply)
+ name = (known after apply)
+ offer_url = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.juju_offer.kratos_info_offer will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "kratos_info_offer" {
+ application_name = "kratos"
+ endpoints = [
+ "kratos-info",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "kratos-info-offer"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.oauth2_proxy.juju_application.application will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "application" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = ""
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "oauth2-proxy"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "oauth2-proxy-k8s"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.postgresql.juju_application.k8s_postgresql will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "k8s_postgresql" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "postgresql-k8s"
+ resources = {}
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ storage_directives = {
+ "pgdata" = "10G"
}
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "14/edge"
+ name = "postgresql-k8s"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.traefik.juju_application.traefik will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "traefik" {
+ config = {
+ "enable_experimental_forward_auth" = "true"
}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "traefik-public"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ storage_directives = {}
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = (known after apply)
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "traefik-k8s"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.module.hydra.juju_application.application will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "application" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "hydra"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "hydra"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.module.hydra.juju_offer.oauth_offer will be created
+ resource "juju_offer" "oauth_offer" {
+ application_name = "hydra"
+ endpoints = [
+ "oauth",
]
+ id = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "oauth-offer"
+ url = (known after apply)
}
# module.iam.module.kratos.juju_application.application will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "application" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "kratos"
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "kratos"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
# module.iam.module.login_ui.juju_application.application will be created
+ resource "juju_application" "application" {
+ config = {}
+ constraints = "arch=amd64"
+ id = (known after apply)
+ machines = (known after apply)
+ model_type = (known after apply)
+ model_uuid = (known after apply)
+ name = "login-ui"
+ resources = {
+ "oci-image" = "ghcr.io/canonical/identity-platform-login-ui:v0.24.2"
}
+ storage = (known after apply)
+ trust = true
+ units = 1
+ charm {
+ base = "ubuntu@22.04"
+ channel = "latest/stable"
+ name = "identity-platform-login-ui-operator"
+ revision = (known after apply)
}
}
Plan: 33 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Terraform will create two Juju models (workspaces). These models are implicitly associated with your existing controller and K8S cloud and hold your deployed, configured, and integrated Identify Platform charmed applications and their charmed dependencies.
This process can take several minutes, depending on your hardware and network speed.
The iam model contains all the crucial identity applications, as explained in the Canonical Identity Platform architecture guide.
And the core model contains all of their shared dependencies:
- Charmed Postgresql: the SQL database of choice
- Charmed Traefik: which will be used for ingress
- Self Signed Certificates: for managing the TLS certificates that our ingress will use.
You can switch between those models using juju switch <iam|core> and track the progress of your deployment by running:
juju status --watch 1s
This command displays the status of the installation and information about the model, like IP addresses, ports, versions etc.
Your deployment is ready when juju status displays the following output:
Model Controller Cloud/Region Version SLA Timestamp
iam my-controller microk8s/localhost 3.6.13 unsupported 14:48:10+01:00
SAAS Status Store URL
forward-auth active local admin/core.forward-auth
ingress active local admin/core.ingress
postgresql active local admin/core.postgresql
send-ca-cert active local admin/core.send-ca-cert
traefik-route active local admin/core.traefik-route
App Version Status Scale Charm Channel Rev Address Exposed Message
hydra v2.3.0 active 1 hydra latest/stable 395 10.152.183.108 no
kratos v1.3.1 active 1 kratos latest/stable 565 10.152.183.114 no
login-ui 0.24.2 active 1 identity-platform-login-ui-operator latest/stable 197 10.152.183.33 no
oauth2-proxy v7.8.1 active 1 oauth2-proxy-k8s latest/stable 24 10.152.183.120 no
Unit Workload Agent Address Ports Message
hydra/0* active idle 10.1.57.159
kratos/0* active idle 10.1.57.150
login-ui/0* active idle 10.1.57.156
oauth2-proxy/0* active idle 10.1.57.134
Offer Application Charm Rev Connected Endpoint Interface Role
kratos-info-offer kratos kratos 565 0/0 kratos-info kratos_info provider
oauth-offer hydra hydra 395 0/0 oauth oauth provider
Integration provider Requirer Interface Type Message
hydra:hydra hydra:hydra hydra_peers peer
hydra:hydra-endpoint-info kratos:hydra-endpoint-info hydra_endpoints regular
hydra:hydra-endpoint-info login-ui:hydra-endpoint-info hydra_endpoints regular
hydra:oauth oauth2-proxy:oauth oauth regular
ingress:ingress oauth2-proxy:ingress ingress regular
kratos:kratos-info login-ui:kratos-info kratos_info regular
kratos:kratos-peers kratos:kratos-peers kratos-peers peer
login-ui:identity-platform-login-ui login-ui:identity-platform-login-ui identity_platform_login_ui_peers peer
login-ui:ui-endpoint-info hydra:ui-endpoint-info login_ui_endpoints regular
login-ui:ui-endpoint-info kratos:ui-endpoint-info login_ui_endpoints regular
oauth2-proxy:forward-auth forward-auth:experimental-forward-auth forward_auth regular
oauth2-proxy:oauth2-proxy oauth2-proxy:oauth2-proxy oauth2_proxy_peers peer
postgresql:database hydra:pg-database postgresql_client regular
postgresql:database kratos:pg-database postgresql_client regular
send-ca-cert:send-ca-cert oauth2-proxy:receive-ca-cert certificate_transfer regular
traefik-route:traefik-route hydra:public-route traefik_route regular
traefik-route:traefik-route kratos:public-route traefik_route regular
traefik-route:traefik-route login-ui:public-route traefik_route regular
Create a user account in Identity Platform
While the Identity Platform supports integrating external identity providers (such as GitHub, Google, or Entra ID), we will use the built-in local provider to keep this tutorial self-contained. You can create a local admin account directly by running the command below, which will generate a password recovery link and code to complete your setup:
juju run kratos/0 create-admin-account email=<your-email> username=<username> -m iam
Open the link, confirm the recovery code, and set a password for your account. Congratulations, your account is ready!
Learn how to set up external identity providers in this guide.
Integrate Identity and Access Proxy with Spark History Server
In this section, you will deploy the Charmed Spark History Server and secure it by integrating with the Identity and Access Proxy.
Deploy Spark History Server
In this part of the tutorial we will deploy the Charmed Spark History Server and integrate it with the S3 integrator charm to use as a storage backend for Spark logs.
See more: Deploy Spark History Server
Before deploying the application, some prerequisites must be met. First, export your MinIO credentials and S3 endpoint as environment variables:
You can run this script to retrieve them.
export S3_ENDPOINT=<ENDPOINT>
export S3_BUCKET=history-server
export ACCESS_KEY=<ACCES_KEY>
export SECRET_KEY=<SECRET_KEY>
Create an S3 bucket named history-server and a path object spark-events to store Spark logs in S3.
This can be done in multiple ways depending on your S3 backend interface.
For instance, you can do it with Python API using boto library:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from botocore.client import Config
import boto3
config = Config(connect_timeout=60, retries={"max_attempts": 0})
session = boto3.session.Session(
aws_access_key_id="<access-key>", aws_secret_access_key="<secret-key>"
)
s3 = session.client("s3", endpoint_url="<s3-endpoint>", config=config)
s3.create_bucket(Bucket="history-server")
s3.put_object(Bucket="history-server", Key=("spark-events/"))
Next, deploy the s3 integrator charm:
juju switch iam
juju deploy s3-integrator --channel edge
juju config s3-integrator bucket=$S3_BUCKET path="spark-events" endpoint=$S3_ENDPOINT
juju run s3-integrator/leader sync-s3-credentials access-key=$ACCESS_KEY secret-key=$SECRET_KEY
Then, deploy the Charmed Spark History Server and relate with s3 integrator:
juju deploy spark-history-server-k8s --channel 3/edge --trust
juju integrate s3-integrator spark-history-server-k8s
Use Identity and Access Proxy to protect Spark History Server access
To expose the Spark History Server while keeping it secure, we will connect it to the ingress controller and enforce authentication via the proxy.
Provide ingress to Spark by running:
juju integrate spark-history-server-k8s ingress
Finally, integrate Spark with the proxy:
juju integrate oauth2-proxy spark-history-server-k8s:oauth2-proxy
These integrations initiate a data flow that propagates configuration parameters across the stack, triggering Charmed Traefik to apply a ForwardAuth middleware to the Spark History Server route, ensuring that every incoming request is authenticated before it reaches the workload.
Validate the integrations
To verify that the integration was successful, try accessing the Spark History Server and check if authentication is required.
Retrieve the public url by running:
juju run traefik-public/0 show-proxied-endpoints --format json -m core | \
jq -r '."traefik-public/0".results."proxied-endpoints" | fromjson | .[] | select(.url | contains("spark-history-server")) | .url'
Go to the retrieved url in a browser and trust the self-signed certificate.
When you access Spark, Traefik asks OAuth2 Proxy whether access to the endpoint is protected. If so, it checks if there is a valid session. In case it doesn’t find one, it will redirect to the Identity Platform login page:
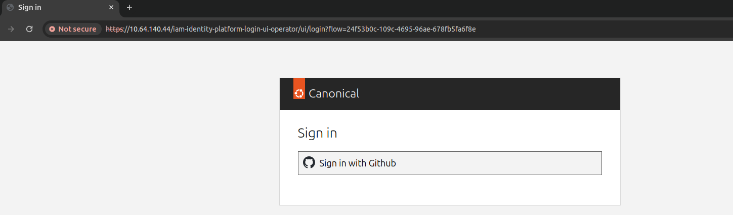
Sign in with the credentials you created earlier in this tutorial.
Upon successful authentication, you will be redirected back to Spark, this time allowed to access the application page. Note that you won’t see any jobs unless you completed one.
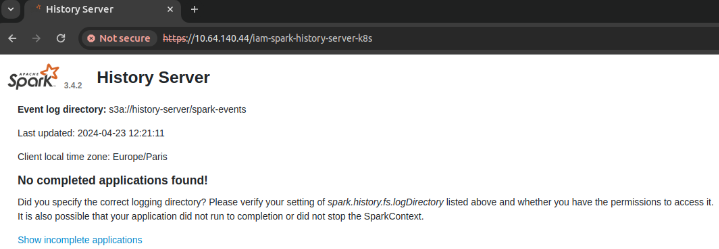
Tear things down
To clean up the resources created during this tutorial, run:
terraform -chdir=examples/auth-proxy destroy
This will remove all charmed applications and destroy the Juju models that were provisioned as part of the deployment.