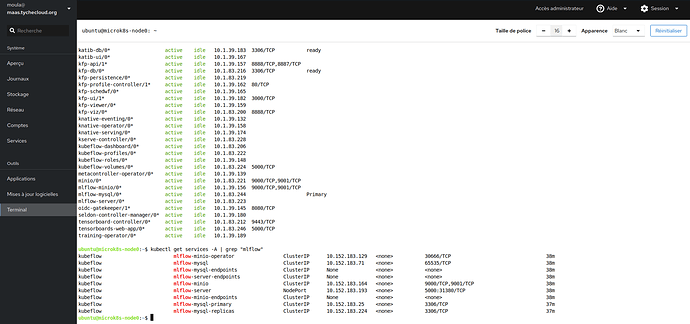
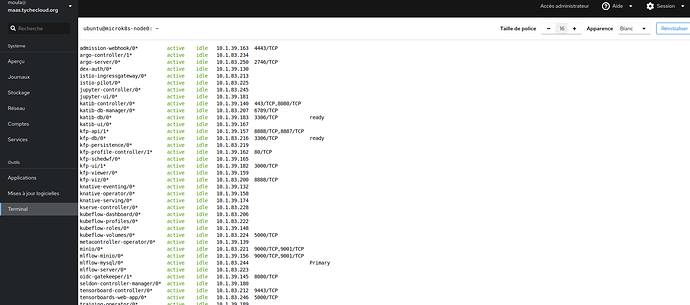
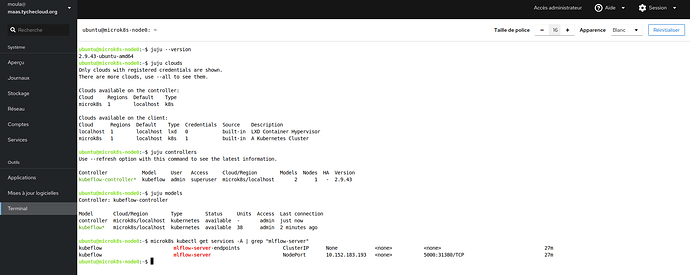
@beliaev-maksim Sorry but the problem is not with the version of juju. Whether it’s version 2.9 or 3.2 the problem is the same. I even find that with juju 3.2 it goes faster on my platform. I have to use the public loadbalancer ip to connect. As with kubeflow 192.168.70.133.npi.io. Deployed with kubeflow you need the link with service/istio-ingressgateway-workload LoadBalancer 10.152.183.192:5000 ( 192.168.70.133.nip.io/mllow/#. Deployed mlflow bundle without kubeflow you have to add traefik-k8s as a gateway for the public ip 192.168.70.133… Thank’s.