Welcome to the guide on how to deploy Charmed MLflow on Charmed Kubernetes. In this guide, we will guide you through the process of connecting Juju to an existing Charmed Kubernetes cluster and deploying the MLflow bundle on top of it.
Prerequisites:
We assume that you have access to a Charmed Kubernetes cluster using kubectl . If you don’t have a cluster set up, you can follow this guide to deploy one on AWS.
Contents
- Install Juju
- Connect Juju to Charmed Kubernetes cluster
- Deploy MLflow bundle
- Connect to MLflow dashboard
Install Juju
Install Juju:sudo snap install juju --classic --channel=2.9/stable
Connect Juju to Charmed Kubernetes cluster
Configure Juju to communicate with the Charmed Kubernetes cluster by creating a controller:juju add-k8s charmed-k8s-aws --controller $(juju switch | cut -d: -f1) \
--storage=cdk-ebs
Create a model. The model name is up to you, in our case we use kubeflow as you might want to connect MLflow with Kubeflow which requires that particular name:
juju add-model kubeflow charmed-k8s-aws
Deploy MLflow bundle
Deploy the MLflow bundle:juju deploy mlflow --channel=2.1/edge --trust
Wait until the deployments are active:
juju-wait -m kubeflow -t 2700
Connect to MLflow dashboard
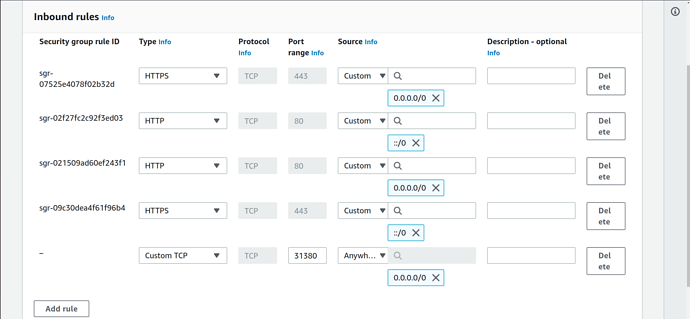
By default, the MLflow UI is exposed as a NodePort Kubernetes service, accessible at each node’s IP address. MLflow runs on port 31380 by default. However, AWS blocks inbound traffic to this port from outside. To overcome this, we need to add an inbound rule to the security group of nodes.To set the security group, list all available nodes in your Kubernetes cluster and choose any EXTERNAL-IP that you will use to access the MLflow UI:
kubectl get nodes -o wide
In your AWS account find the EC2 instance with that particular EXTERNAL-IP and enable access to the port 31380 in the inbound rules of the security group. You can use this guide for the setup.
Open a web browser and visit <nodes-ip-address>:31380 to access the MLflow UI.